
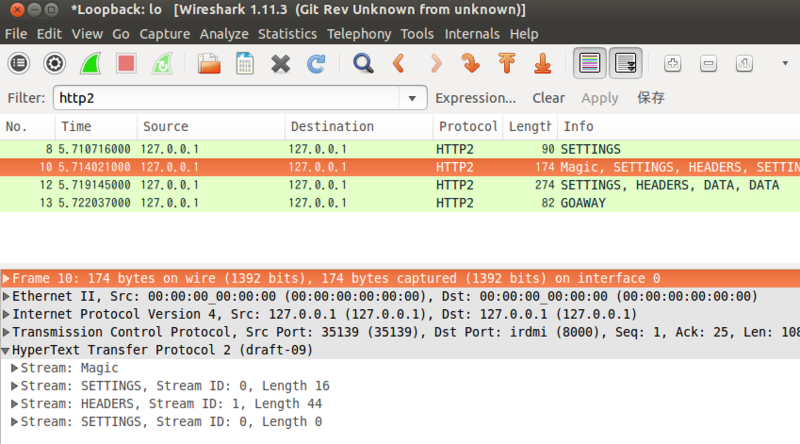

So if you want to make an insecure HTTP/2 connection, the browser just has to somehow already know that the server supports HTTP/2, and it needs to simply establish the TCP connection and then start with an HTTP/2 Connection Preface.
You specifically want to look at Section 3, "Starting HTTP/2". This is covered in the HTTP/2 specification, the latest version of which, as of this writing, is RFC 9113. The client (browser) just has to somehow already know that the server supports HTTP/2, and once the insecure TCP handshake completes, the client should start the connection with an HTTP/2 Connection Preface, which the server should respond to with its own HTTP/2 Connection Preface, and both sides should continue to do HTTP/2 from that point on. Then after TLS negotiation completes, both sides exchange HTTP/2 Connection Prefaces and continue to do HTTP/2 from that point on.įor insecure connections, the intent to do HTTP/2 is not negotiated at all any more (and maybe never was). For secure connections, the intent to do HTTP/2 is negotiated during the TLS negotiation, via TLS-ALPN.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
